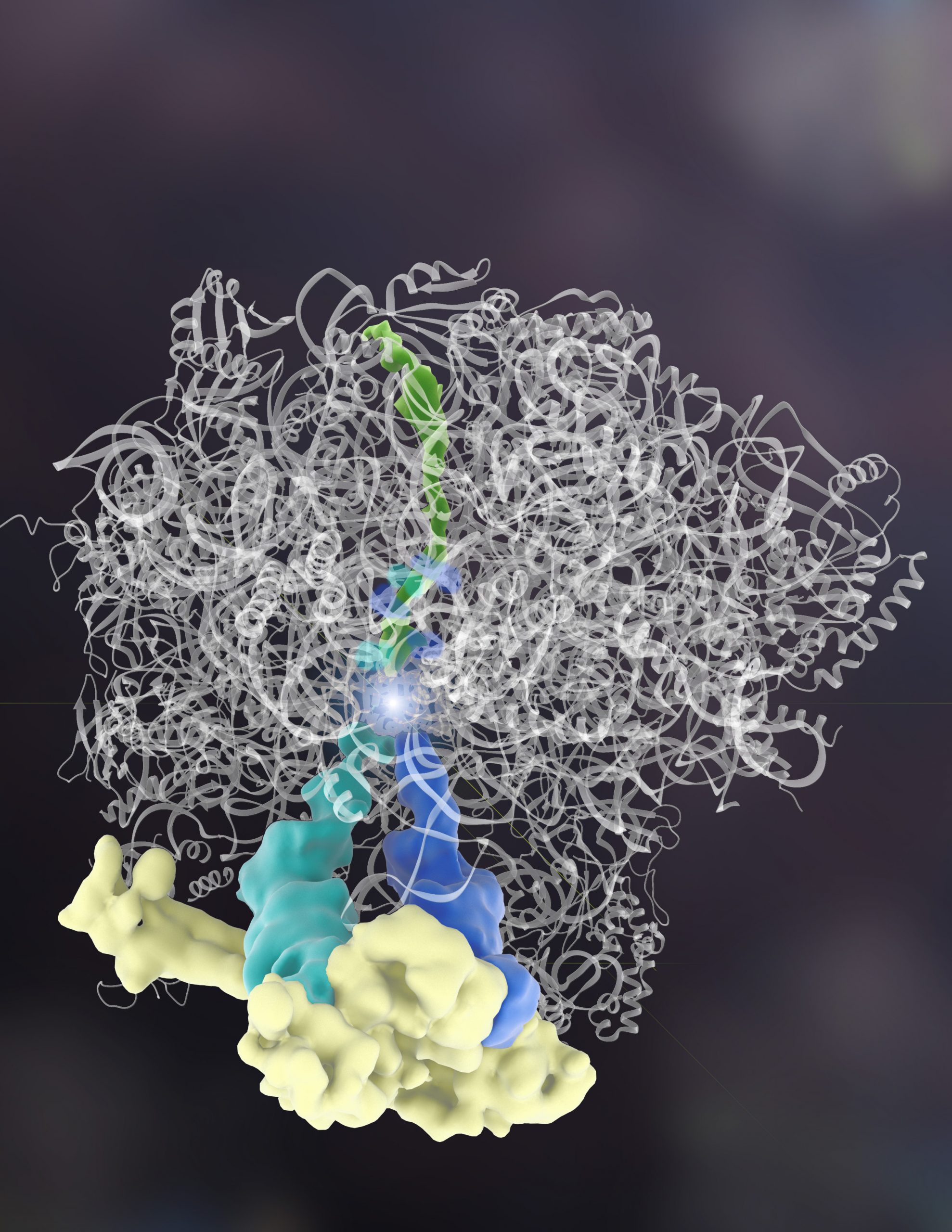
Open any introductory biology textbook and one of the first things you’ll learn is that our DNA spells out the instructions for making proteins, tiny machines that do much of the work in our body’s cells. Results from a study published on Jan. 2 in Science defy textbook science, showing for the first time that the building blocks of a protein, called amino acids, can be assembled without blueprints – DNA and an intermediate template called messenger RNA (mRNA). A team of researchers has observed a case in which another protein specifies which amino acids are added.
